Are We Becoming a Regressive Society? Supreme Court Stays New UGC Equity Rules
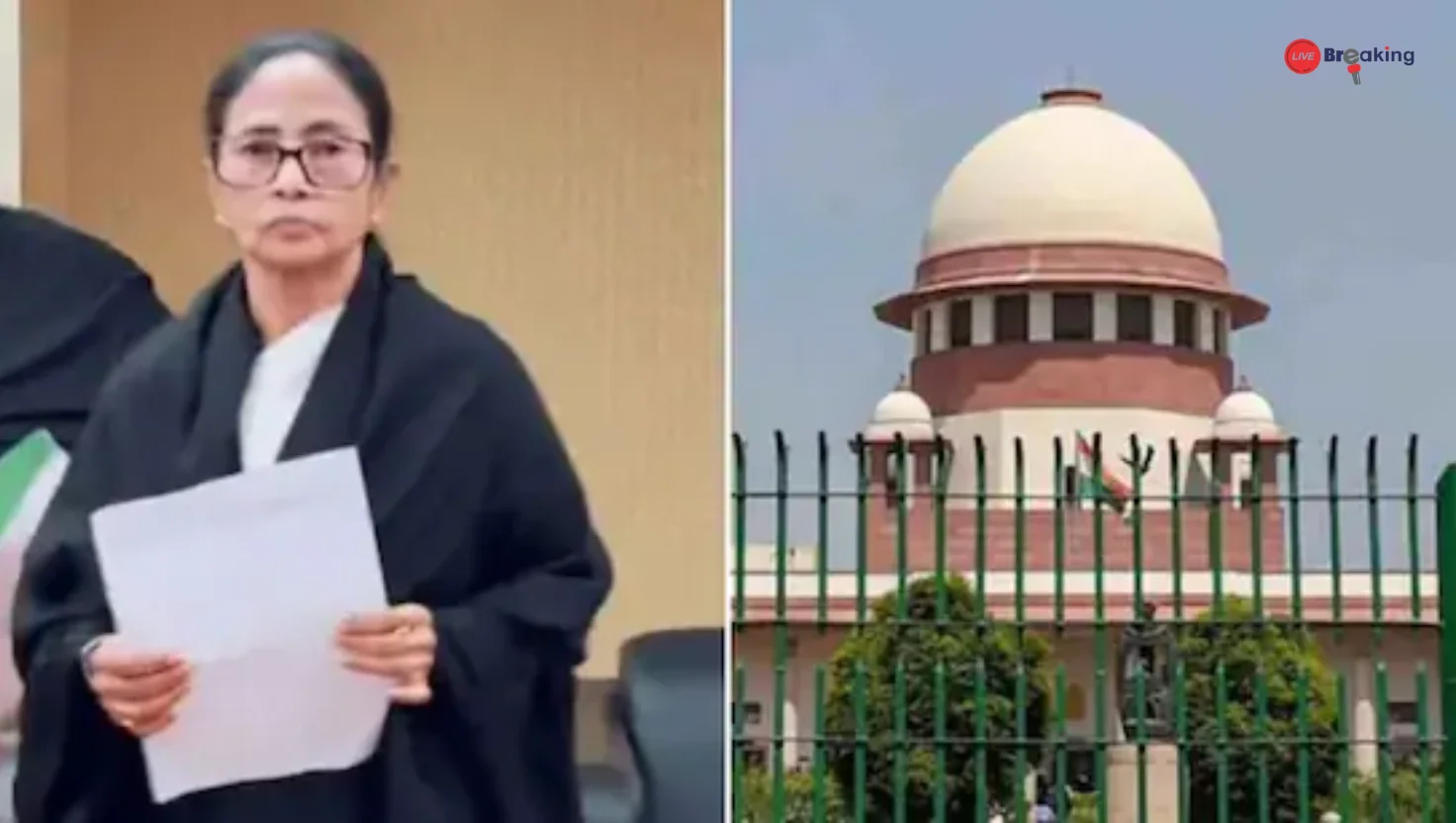
The recent decision by the Supreme Court of India to stay the new equity-related regulations proposed by the University Grants Commission (UGC) has sparked a nationwide debate. At the heart of the controversy lies a pressing question: Are we moving forward as a progressive democracy, or drifting toward a regressive social framework that undermines inclusion and constitutional values?
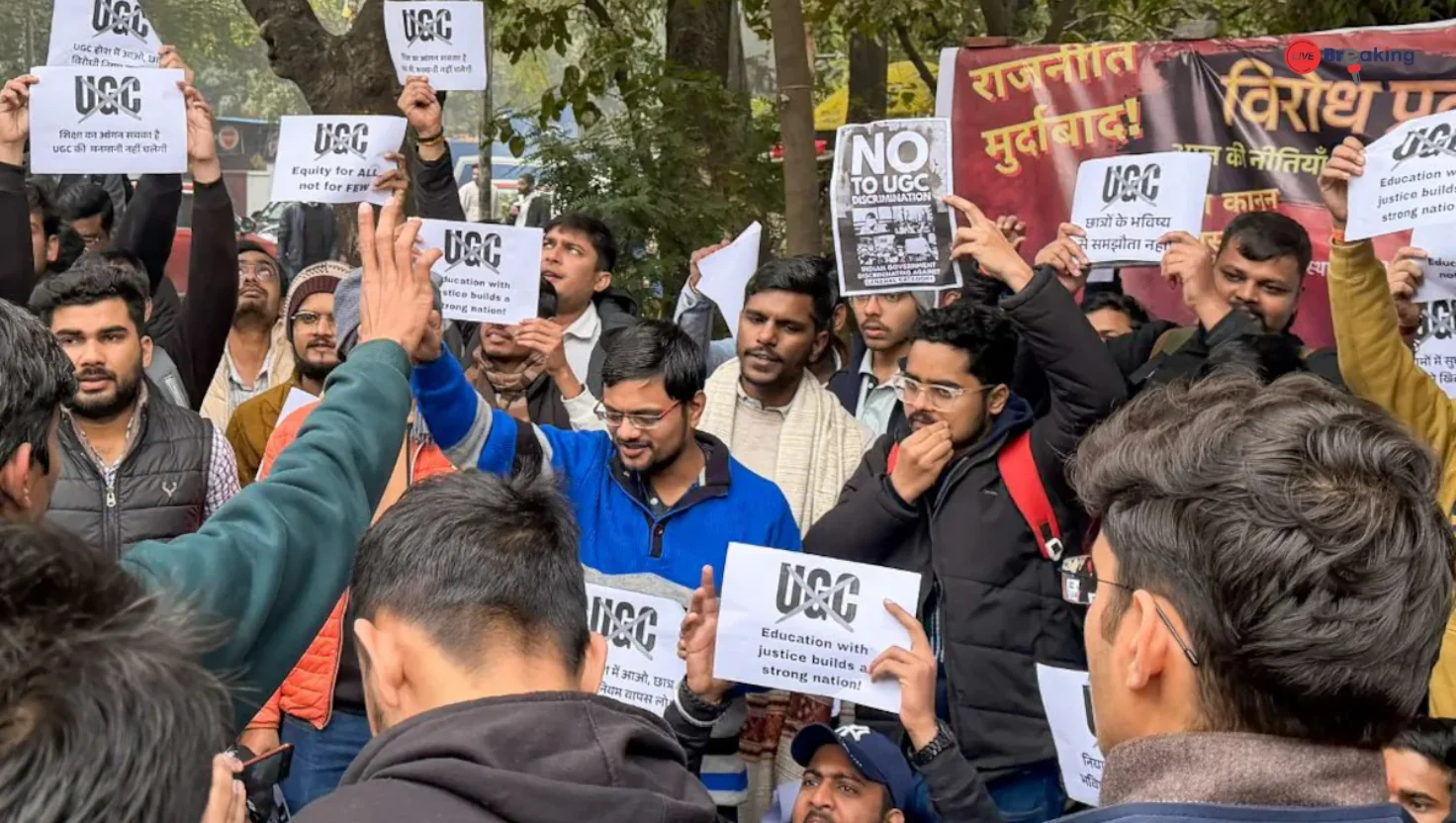
The apex court’s strong observations—particularly its remark on the “complete vagueness” of the rules—have brought temporary relief to students, educators, and activists who feared the long-term consequences of these regulations on India’s higher education ecosystem.
What Are the New UGC Equity Rules?
The stayed rules were introduced by the UGC with the stated objective of reforming and standardizing faculty recruitment and governance structures in universities. However, critics argued that the regulations diluted long-established principles of social justice, especially those related to representation, diversity, and institutional autonomy.
Key concerns raised included:
-
Lack of clarity in definitions and implementation mechanisms
-
Potential weakening of affirmative action policies
-
Excessive centralization of power
-
Reduced role of academic bodies in decision-making
These ambiguities triggered widespread protests across university campuses, with many alleging that the rules could disproportionately affect marginalized communities.
Supreme Court’s Intervention: Why It Matters
While hearing petitions challenging the regulations, the Supreme Court expressed serious reservations about their drafting and intent. The court noted that laws and regulations impacting fundamental rights must be precise, transparent, and constitutionally sound.
By staying the rules, the court has:
-
Prevented immediate implementation that could cause irreversible harm
-
Reaffirmed the importance of clarity in policymaking
-
Opened the door for wider consultation and debate
The interim stay underscores the judiciary’s role as a constitutional guardian, especially when executive decisions raise questions about equality and fairness.
A Larger Debate: Progress vs Regression
The controversy has reignited a broader conversation about the direction India’s education policy is taking. Education has historically been a tool for social mobility and empowerment. Any policy perceived as rolling back hard-earned safeguards naturally invites strong resistance.
Many academics argue that instead of empowering institutions, the new rules risk creating a uniform, top-down model that ignores India’s social diversity. Student groups, on the other hand, see this as part of a pattern where voices from the ground are sidelined in favor of bureaucratic efficiency.
This raises a fundamental question: Can reforms truly be called reforms if they weaken inclusion and participation?
Impact on Students and Universities
The immediate impact of the court’s stay is a sense of relief across campuses. Recruitment processes, governance structures, and academic operations can continue under existing norms until a final decision is reached.
However, uncertainty remains. Universities are now caught between reform pressures and legal scrutiny. Students worry about delays, while faculty members seek assurances that autonomy and academic freedom will not be compromised in the long run.
What Happens Next?
The Supreme Court’s stay is not the final word. The case will continue, and the UGC may be asked to revisit, clarify, or even rewrite the regulations. Legal experts believe this could lead to:
-
Broader stakeholder consultations
-
More transparent drafting processes
-
A better balance between reform and rights
Ultimately, the outcome could set an important precedent for how education policies are framed in the future.
FAQs
Why did the Supreme Court stay the new UGC equity rules?
The court found the rules to be vague and lacking clarity, especially since they could impact fundamental rights related to equality and representation.
Do the stayed rules affect current university admissions or exams?
No. The stay mainly affects governance and recruitment-related provisions, not ongoing admissions or examinations.
Are the UGC rules scrapped permanently?
No. They are only stayed for now. The final decision will come after detailed hearings.
Why are students and teachers protesting these rules?
Protesters fear the rules could dilute affirmative action, reduce institutional autonomy, and negatively impact marginalized groups.
What does this mean for higher education reforms in India?
It signals that reforms must be inclusive, transparent, and constitutionally valid, with proper stakeholder consultation.
Conclusion
The Supreme Court’s decision to stay the new UGC equity rules has provided a critical pause in an increasingly polarized debate. Whether India emerges stronger and more inclusive from this moment depends on how policymakers respond—by listening, revising, and reaffirming the constitutional promise of equality. The question remains open, but the message is clear: progress cannot come at the cost of justice.